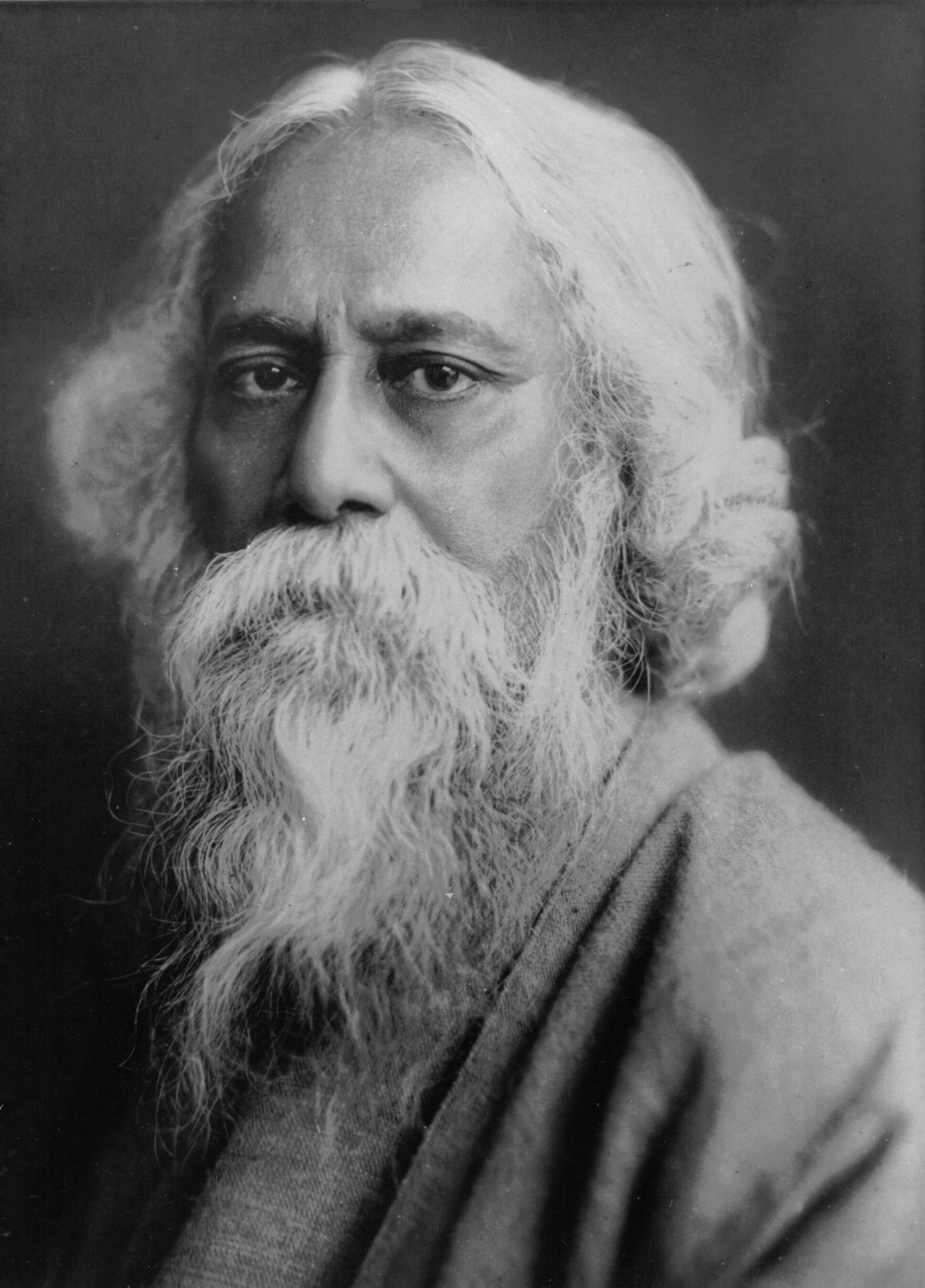

Rabindranath Tagore was a Bengali polymath who reshaped Bengali literature and music, as well as Indian art with Contextual Modernism in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Author of Gitanjali and its "profoundly sensitive, fresh and beautiful verse", he became the first non-European to win the Nobel Prize in Literature in 1913.
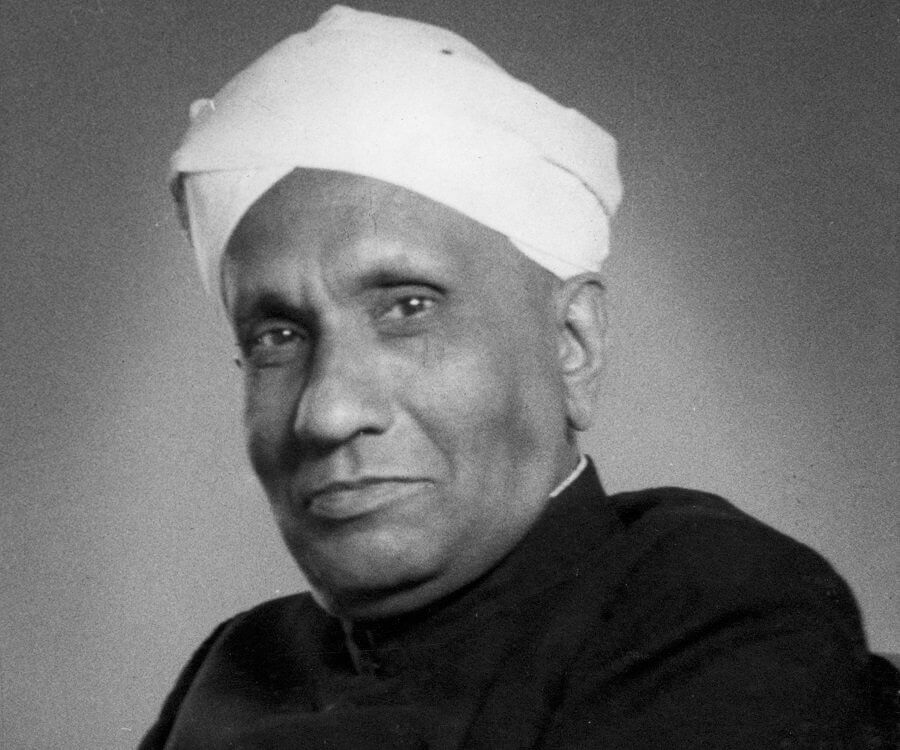

Sir Chandrasekhara Venkata Raman was an Indian physicist born in the former Madras Province in India presently called as Tamil Nadu, who carried out ground-breaking work in the field of light scattering, which earned him the 1930 Nobel Prize for Physics. He discovered that when light traverses a transparent material, some of the deflected light changes wavelength. This phenomenon, subsequently known as Raman scattering, results from the Raman effect. In 1954, India honoured him with its highest civilian award, the Bharat Ratna.

Amartya Kumar Sen, CH, FBA is an Indian economist and philosopher, who since 1972 has taught and worked in the United Kingdom and the United States. Sen has made contributions to welfare economics, social choice theory, economic and social justice, economic theories of famines, and indexes of the measure of well-being of citizens of developing countries.
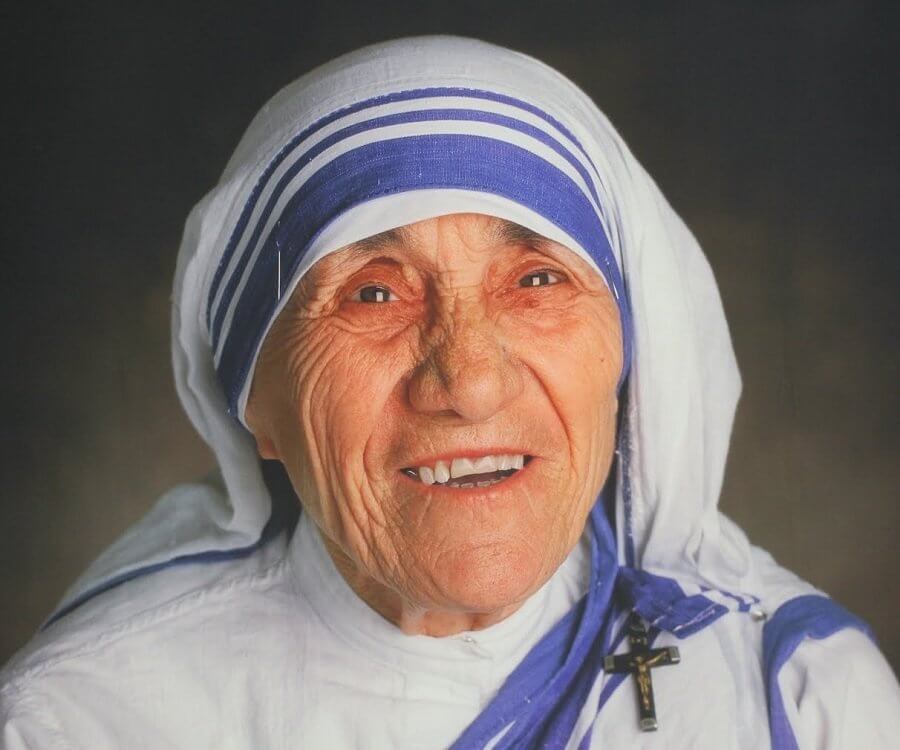

Mother Teresa, known in the Catholic Church as Saint Teresa of Calcutta was an Albanian-Indian[2] Roman Catholic nun and missionary.[5] She was born in Skopje (now the capital of the Republic of Macedonia), then part of the Kosovo Vilayet of the Ottoman Empire. After living in Macedonia for eighteen years she moved to Ireland and then to India, where she lived for most of her life.
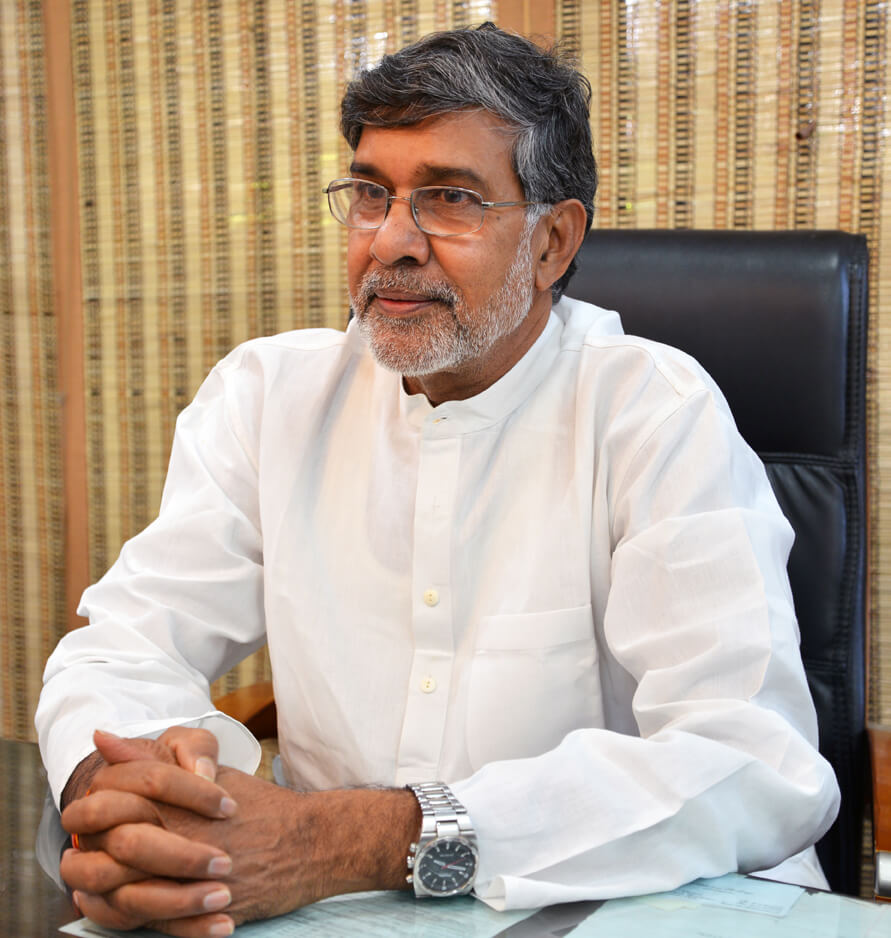

Kailash Satyarthi is an Indian children's rights and education advocate and an activist against child labour. He founded the Bachpan Bachao Andolan in 1980 and has acted to protect the rights of more than 83,000 children from 144 countries. It is largely because of Satyarthi's work and activism that the International Labour Organization adopted Convention No. 182 on the worst forms of child labour, which is now a principal guideline for governments around the world. His work is recognized through various national and international honours and awards including the Nobel Peace Prize of 2014, which he shared with Malala Yousafzai of Pakistan.
We mix all detailed things together
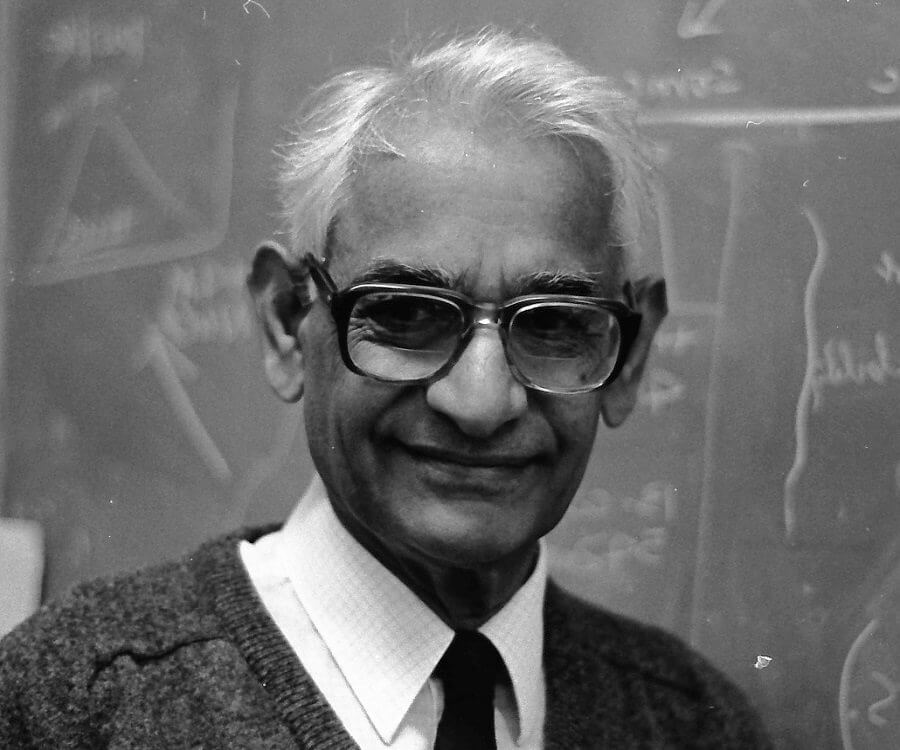
Khorana was born in Raipur, British India. He served on the faculty of the University of British Columbia from 1952-1960, where he initiated his Nobel Prize winning work. He became a naturalized citizen of the United Statesin 1966, and subsequently received the National Medal of Science. He co-directed the Institute for Enzyme Research, became a professor of biochemistry in 1962 and was named Conrad A. Elvehjem Professor of Life Sciences at University of Wisconsin–Madison.

Subrahmanyan Chandrasekhar was an Indian American astrophysicist who was awarded the 1983 Nobel Prize for Physics with William A. Fowler"for his theoretical studies of the physical processes of importance to the structure and evolution of the stars". His mathematical treatment of stellar evolution yielded many of the best current theoretical models of the later evolutionary stages of massive stars and black holes. The Chandrasekhar limit is named after him.
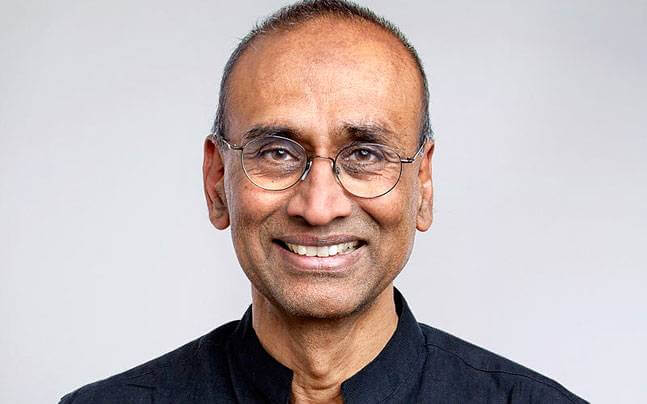

Venkatraman "Venki" Ramakrishnan (born 1952) is an Indian-American-British structural biologist of Indian origin. He is the current President of the Royal Society, having held the position since November 2015. In 2009 he shared the Nobel Prize in Chemistry with Thomas A. Steitz and Ada Yonath, "for studies of the structure and function of the ribosome".
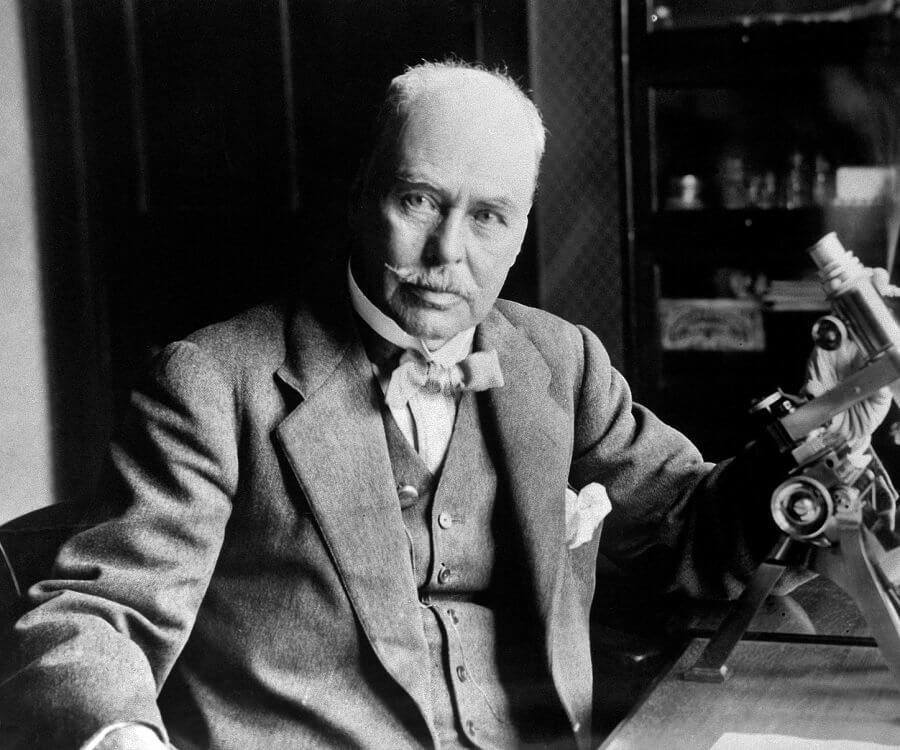

Sir Ronald Ross was a British medical doctor who received the Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine in 1902 for his work on the transmission of malaria, becoming the first British Nobel laureate, and the first born outside of Europe. His discovery of the malarial parasite in the gastrointestinal tract of a mosquito proved that malaria was transmitted by mosquitoes, and laid the foundation for the method of combating the disease. He was a polymath, writing a number of poems, published several novels, and composed songs. He was also an amateur artist and natural mathematician. He worked in the Indian Medical Service for 25 years.
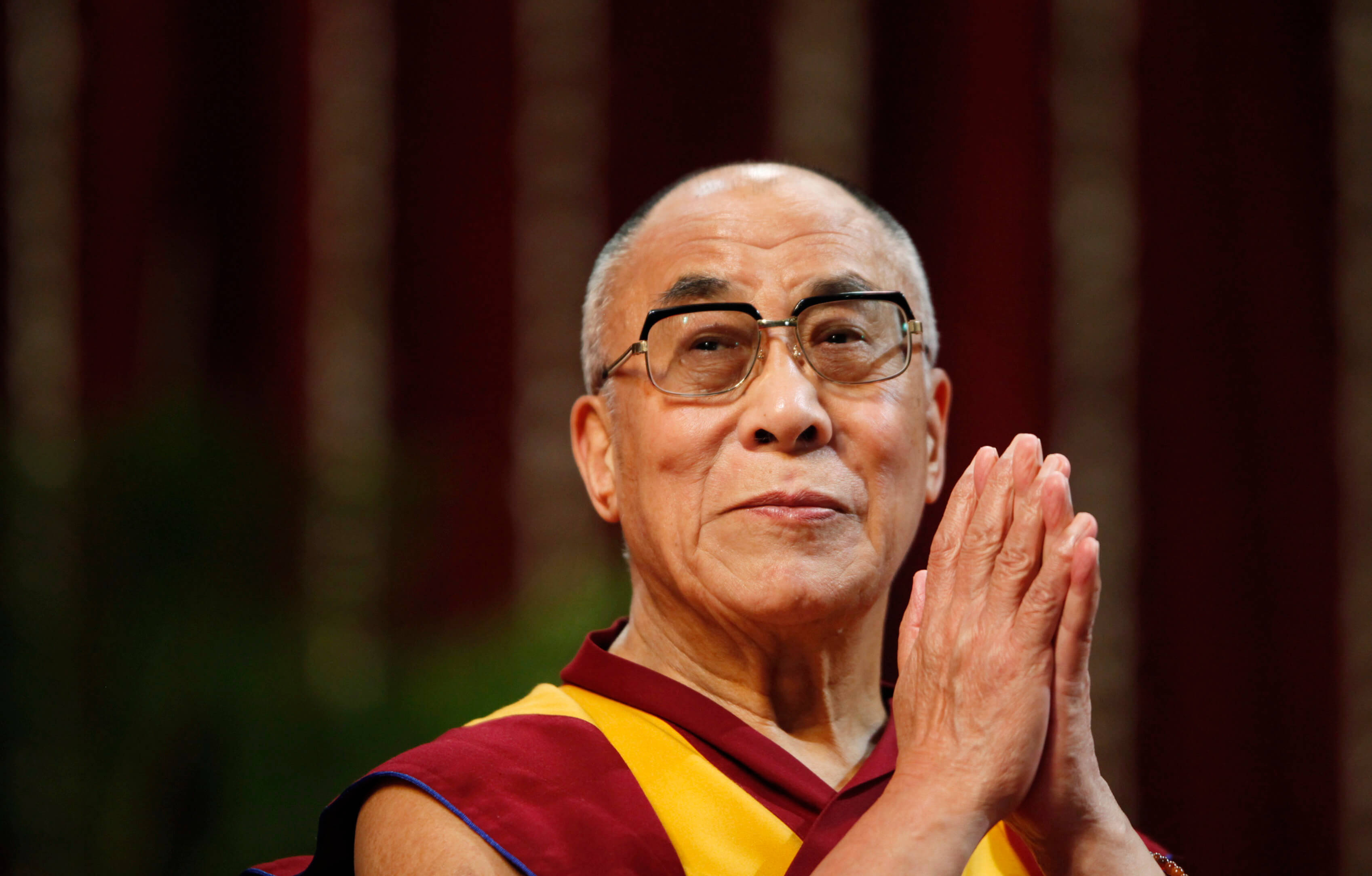

The 14th Dalai Lama is the current Dalai Lama. During the 1959 Tibetan uprising, the Dalai Lama fled to India, where he currently lives as a refugee. The 14th Dalai Lama received the Nobel Peace Prize in 1989. He has traveled the world and has spoken about the welfare of Tibetans, environment, economics, women's rights, non-violence, interfaith dialogue, physics, astronomy, Buddhism and science, cognitive neuroscience, reproductive health, and sexuality, along with various Mahayana and Vajrayana topics.
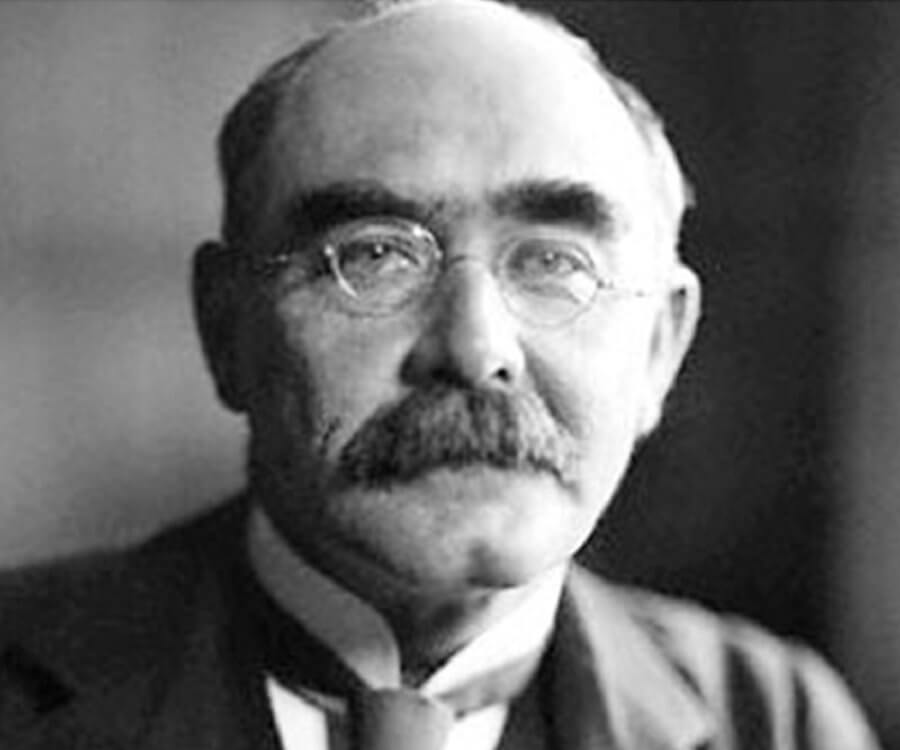

Kipling was one of the most popular writers in the United Kingdom, in both prose and verse, in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Henry James said: "Kipling strikes me personally as the most complete man of genius, as distinct from fine intelligence, that I have ever known." In 1907, at the age of 42, he was awarded the Nobel Prize in Literature, making him the first English-language writer to receive the prize and its youngest recipient to date. He was also sounded out for the British Poet Laureateship and on several occasions for a knighthood, both of which he declined. Rudyard Kipling was born on December 30, 1865, in Bombay, India. He was educated in England but returned to India in 1882. A decade later, Kipling married Caroline Balestier and settled in Brattleboro, Vermont, where he wrote The Jungle Book (1894), among a host of other works that made him hugely successful.
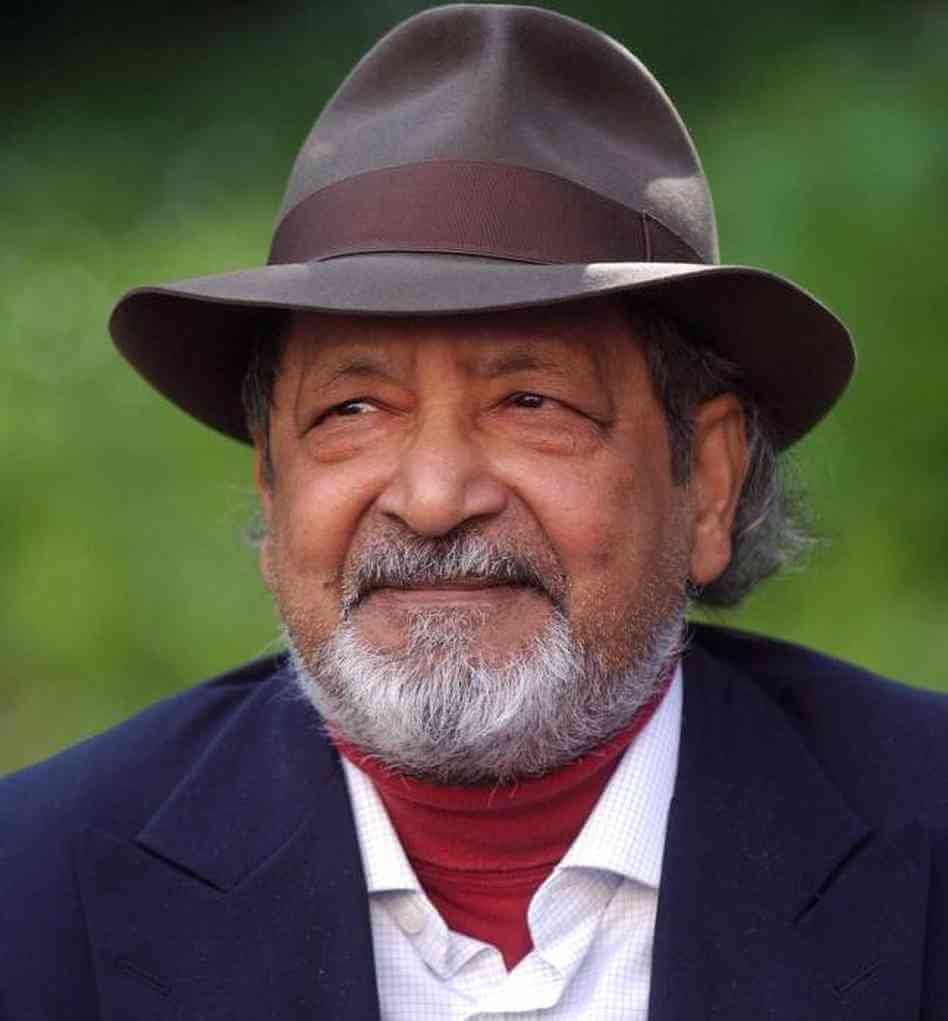

Sir Vidiadhar Surajprasad Naipaul is a Nobel Prize-winning, Indian-origin British author who was born in Trinidad. He is known for his comic early novels set in Trinidad and Tobago, his bleaker later novels of the wider world, and his autobiographical chronicles of life and travels. He has published more than thirty books, both of fiction and nonfiction, over some fifty years.